Central Serous Retinopathy
What is Central Serous Retinopathy? (What is CSR?)
Central Serous Retinopathy, abbreviated name CSR, refers to fluid accumulation below the retina. The disease is defined as 'Central' Serous Retinopathy because it usually affects the fovea (visual point) and disrupts central vision. It is also called Central Serous Chorioretinopathy because of the origin of the fluid is choroid.
What is the cause of Central Serous Retinopathy?
The exact cause of central serous retinopathy has not been determined. The high pressure of the choroid, which contains the vessels feeding the outer part of the retina, is thought to be the cause of deterioration of the retinal pigment epithelium. Fluid builds up under retina due to hypofunction of retinal pigment epithelium.
Who is at risk for Central Serous Retinopathy?
CSR can be seen in all individuals aged 20 to 80 years. It is most commonly seen in men aged 30-50 years.
What are the risk factors for the development of Central Serous Retinopathy?
The most important risk factor for CSR development is the psychological stress. Therefore, it is known by most patients as fluid accumulation at the visual point due to the stress. Males are at least five times more likely to develop CSR. Other reported risk factors for central serous retinopathy are;
1. Type A personality
2. Use of steroids
3. Smoking
4. Sleep apnea
5. Pregnancy
6. Insomnia
7. Hypertension
8. Chronic excessive caffeine intake
What is the symptoms of Central Serous Retinopathy?
The patients with Central Serous Retinopathy may present with complaints of wavy and blurred vision, blind spot in the center, objects appearing smaller, farther and pale.
Does Central Serous Retinopathy cause permanent visual loss?
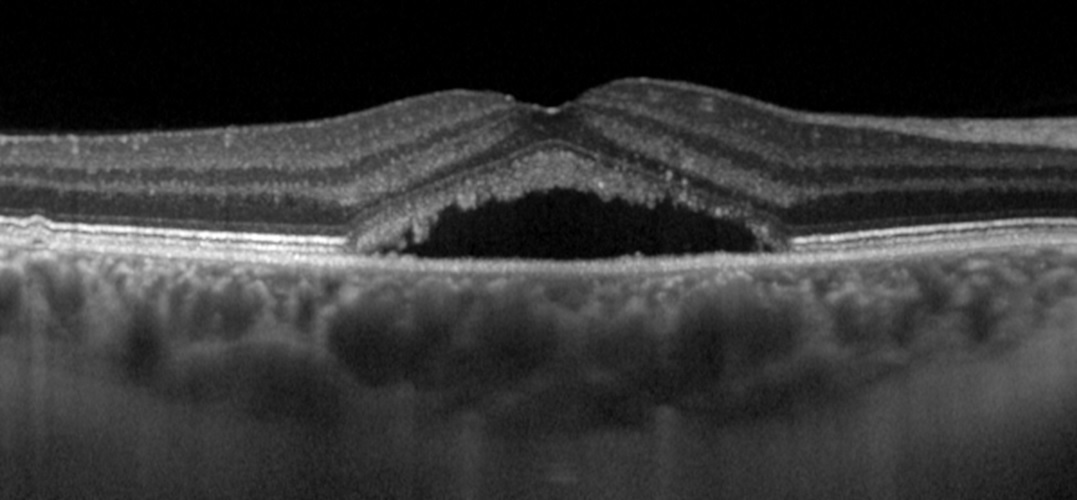
In Central Serous Retinopathy, the fluid below fovea usually disappears spontaneously within 3 months. In 1/3 of the patients CSR proceeds with recurrences. As soon as liquid is collected under the retina, the photoreceptor (visual cell) disruption begins. If the fluid at the central area does not disappear within 3 months, a noticeable reduction in visual function occurs. In addition, every new attack reduces the visual slightly. If the disease progresses to Chronic Central Serous Retinopathy, the visual acuity may be permanently reduced.
How is Central Serous Retinopathy diagnosed?
For the diagnosis of Central Serous Retinopathy, a routine eye examination is followed by posterior segment examination with pupil dilatation. Optic coherence tomography (OCT), using light waves to visualize the retina without any side effects, is performed in patients suspected of CSR. In addition, it is necessary to perform fluorescein angiography and indocyanine green angiography in cases where CSR therapy should be applied.
What is the treatment of Central Serous Retinopathy ?
CSR is a self-limiting disease. If the patient is using corticosteroid medication, it is desirable to quit and stay away from the stress. However, if the fluid under the retina does not disappear within 3 months, it should be treated. The most effective method for central serous retinopathy treatment is photodynamic therapy preferred by our clinic. Photodynamic therapy is applied to foci determined by fluorescein angiography and indocyanine green angiography. Photodynamic therapy is the only method that reduces the recurrence frequency in CSR.
Last Updated: October 23, 2024